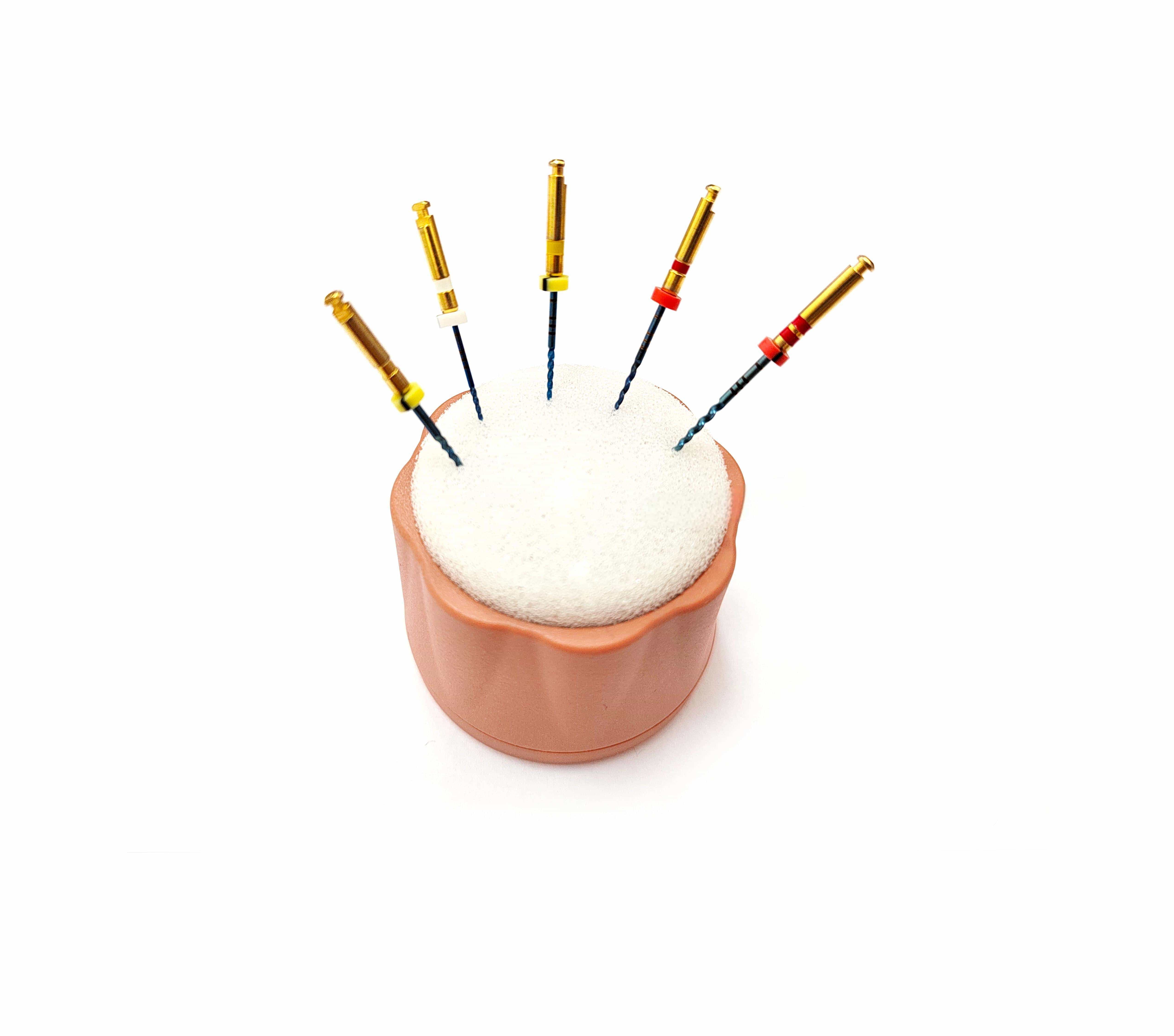
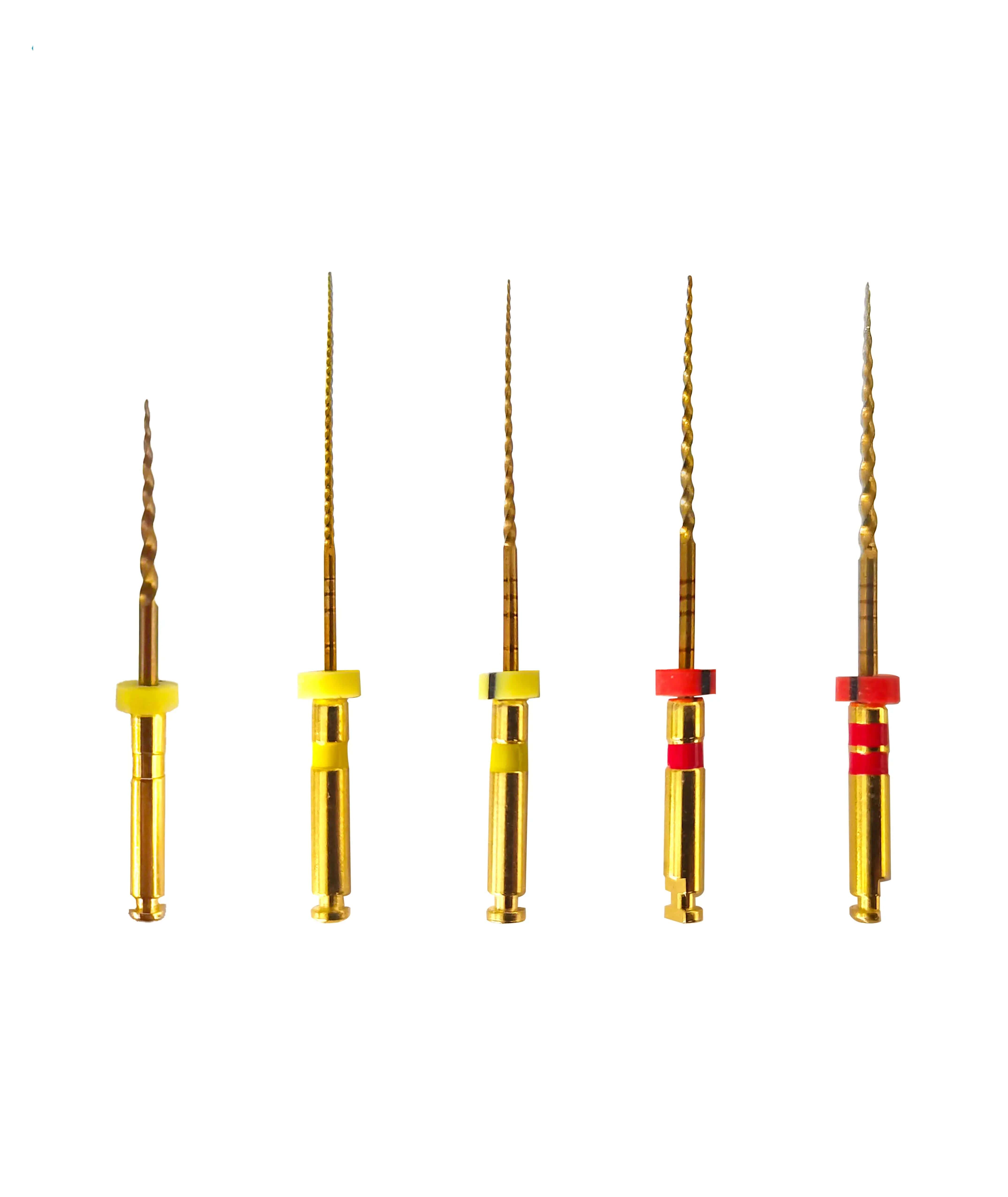
Endodontic Rotary Files: Comprehensive Guide to Types, Uses, and Best Practices
Endodontic rotary files, commonly referred to as endo rotary files, have become a cornerstone in contemporary endodontic treatment. These mechanical instruments are specifically designed for root canal procedures, allowing clinicians to effectively clean, shape, and enlarge the canal system to facilitate optimal disinfection and obturation. Over the years, advancements in rotary file technology have not only improved clinical outcomes but have also streamlined procedures, reducing operator fatigue and procedural errors. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of endodontic rotary files, their applications, advantages, and best practices, as well as the latest innovations shaping the future of endodontics.
What Are Endodontic Rotary Files?
Endodontic rotary files are specialized dental instruments used to mechanically clean and shape root canals during endodontic treatment. They are typically made from high-grade materials like nickel-titanium (NiTi) and stainless steel, offering enhanced flexibility, strength, and cutting efficiency. Unlike traditional hand files, rotary files are powered by an electric motor, allowing for precise, controlled movements that significantly reduce procedural time and operator fatigue.
Key Features of Endodontic Rotary Files:
- Nickel-Titanium Composition: NiTi files are known for their superior flexibility, which enables them to navigate curved canals without causing canal transportation or ledging.
- Variable Taper Designs: Dental rotary files come in different tapers (e.g., 0.04, 0.06) to effectively shape canals while maintaining structural integrity.
- Controlled Speed and Torque: Modern endo motors offer customizable settings, allowing clinicians to adjust speed and torque based on specific file systems and clinical requirements.
- Enhanced Cutting Efficiency: With advanced flute designs and cutting edges, rotary files can efficiently remove dentin, infected tissue, and debris, creating a smooth canal path for obturation.
.png)
Types of Endodontic Rotary Files
The classification of endodontic rotary files is based on factors such as material composition, design, application, and usage protocol. Here is an expanded overview of the most commonly used types:
Stainless Steel Rotary Files:
Made from rigid stainless steel, these files are best suited for straight or minimally curved canals. While cost-effective, they lack the flexibility of NiTi files and are more prone to causing canal transportation.
Advantages: High cutting efficiency, cost-effective
Disadvantages: Limited flexibility, increased risk of fracture
Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Rotary Files:
NiTi files are highly flexible and exhibit superior cyclic fatigue resistance, making them ideal for navigating curved or complex canal anatomies. Their memory shape property allows them to maintain canal curvature without compromising canal integrity.
Advantages: Excellent flexibility, reduced fracture risk, superior canal centering
Disadvantages: Higher cost compared to stainless steel files
Single-Use Rotary Files:
These files are designed for single-patient use, significantly reducing the risk of cross-contamination. They are pre-sterilized and discarded after use, ensuring optimal cutting efficiency and reducing instrument fatigue.
Advantages: Reduced cross-contamination, optimal sharpness
Disadvantages: Increased cost per procedure
Multifile Systems:
Multifile systems consist of multiple files used sequentially, each with a different taper and diameter to progressively shape the canal. These systems offer greater versatility for handling complex canal anatomies.
Advantages: Customizable, effective for complex anatomies
Disadvantages: Longer procedure time, more inventory required
Reciprocating Files:
Unlike conventional rotary files that rotate continuously, reciprocating files move in a back-and-forth motion, reducing stress on the file and minimizing the risk of separation. This technique is particularly useful for severely curved canals.
Advantages: Reduced cyclic fatigue, improved debris removal
Disadvantages: Requires specialized motor settings
Applications of Endodontic Rotary Files
Endodontic rotary files are integral to the following clinical applications:
- Cleaning and Shaping: Efficiently remove infected pulp tissue, debris, and necrotic material from the root canal system.
- Canal Preparation: Create a conical shape that facilitates optimal irrigation and obturation.
- Retreatment Cases: Used to remove old gutta-percha, posts, or broken instruments.
- Apex Locating: Assist in accurately determining working length in conjunction with electronic apex locators.
Benefits of Using Endo Rotary Files
The incorporation of rotary files into endodontic procedures offers numerous clinical advantages:
Enhanced Cleaning Efficiency: Advanced flute designs and cutting edges improve debris removal and shaping efficiency.
Reduced Operator Fatigue: Automated rotary systems decrease manual labor, allowing clinicians to focus on precision.
Consistent Canal Shaping: Rotary files maintain uniform taper throughout the canal, reducing procedural errors.
Minimized Canal Transportation: Flexible NiTi files effectively navigate curves without distorting the canal shape.
Common Complications and Solutions
File Separation: Avoid excessive torque, inspect files for signs of fatigue, and use glide path files to prevent binding.
Canal Transportation: Utilize flexible NiTi files, avoid aggressive filing, and maintain proper canal curvature.
Ledging or Perforation: Employ smaller files to establish glide paths, avoid excessive apical pressure, and maintain patency throughout the procedure.
Latest Innovations in Endodontic Rotary Files
Enhanced Metallurgy: Heat-treated NiTi alloys offer increased flexibility and cyclic fatigue resistance.
Hybrid Systems: Combining rotary and reciprocating motions to optimize canal shaping.
Advanced Flute Designs: Dual-tapered or variable-pitch designs improve cutting efficiency and debris removal.
Conclusion
Endodontic rotary files have become an essential component of successful root canal therapy, offering precise canal shaping and effective debris removal. By understanding the different types of rotary files, their specific applications, and the latest advancements in file technology, dental professionals can optimize treatment outcomes and ensure patient safety. Staying updated on emerging trends and implementing best practices can further elevate the clinical performance and longevity of endo rotary files.
Read More: Dental Root Canal and Crown: Comprehensive Guide
Contact Us
+86 13651660950
+86 13816828040
peter.chen@comlea.cn
lu.l@comlea.cn
Lane 599, 1# 810,Shuangdan Road, Jiading District, Shanghai





